Macroeconomic conditions1
Global economic growth was moderate in 2023. Thanks to strong private consumption and resilient labor markets, it reached 3.3% according to current estimates. Global economic activity was supported by emerging markets, including China, and, among the industrialized countries, by the United States in particular. The latest data provides mixed signals for the major economies. While real GDP growth in the third quarter of 2023 increased in both China and the United States, it remained unchanged in other industrialized countries due to continued high inflation and its impact on economic activity and consumption.
While consumer behavior continued to normalize after the pandemic, global trade growth in 2023 remained comparatively weak at 1.1% according to current estimates, but already showed signs of improvement in the latter part of the year. The overall weak trade was due to less trade-friendly growth in the global economy, with consumption accounting for a larger share of domestic demand and emerging markets making a greater contribution. In addition, trade growth in the reporting year was also slowed by the recovery in the consumption of services as a result of the complete lifting of COVID-19 restrictions.
Global inflation, measured on the basis of the global consumer price index (CPI), continued to fall over the course of the year. This development was supported by lower energy and food prices while core inflation remained high. In the member states of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), CPI inflation fell to 5.6% in October 2023.
Global financing conditions initially fluctuated in 2023, but ultimately showed a slight improvement in the industrialized countries after inflation remained slightly below expectations in several economies. In addition, some central banks had recently become more cautious with regard to the question of whether further interest rate hikes were necessary.
1 European Central Bank, 2023
Healthcare industry
The healthcare sector is one of the world's largest industries and we are convinced that it demonstrates excellent growth opportunities.
The main growth factors are:
- rising medical needs deriving from aging populations,
- the growing number of chronically ill and multimorbid patients,
- stronger demand for innovative products and therapies,
- advances in medical technology,
- the growing health consciousness, which increases the demand for healthcare services and facilities, and
- the increasing demand for digital health services for patients.
In the emerging countries, additional drivers are:
- expanding availability and correspondingly greater demand for basic healthcare, and
- increasing national incomes and hence higher spending on healthcare.
Overall, OECD countries1 spent an average of 9.2% of their GDP on healthcare services in 2022 (2021: 9.7%). The decline in the share compared to 2021 reflects lower spending to combat the COVID-19 pandemic on the one hand and the impact of rising inflation on the other, which reduces the value of healthcare spending. Despite these factors, the average share of healthcare expenditure in national income in OECD countries was still significantly higher in 2022 than before the pandemic (2019: 8.8%).
The United States recorded the highest expenditure per capita with an estimated US$12,555 in 2022 (2021: US$12,197). Based on current estimates, Germany ranks third in the OECD country comparison with US$8,011 in 2022 (2021: US$7,518). On average, the OECD countries financed 76% of their healthcare expenditure from public funds in 2022. In Germany, this share was 87% in 2022 according to current OECD estimates (2021: 86%).
Average life expectancy has risen in most OECD countries in recent decades. In 2021, it averaged 80.3 years (2020: 80.6 years). The reasons for this are better living conditions, more intensive healthcare, and advances in medical care.
In order to limit the constantly rising expenditure in the healthcare system, cost bearers are increasingly reviewing care structures to identify potential savings. However, rationalization alone cannot compensate for the rise in costs. For this reason, market-based incentives for cost- and quality-conscious action in the healthcare sector should also be created. In this way, treatment costs can be reduced by improving the overall quality of care. As a result, prevention programs are becoming just as important as innovative remuneration models that are linked to the quality of treatment. The digitalization of the healthcare system in particular can also contribute to improved patient care and greater cost efficiency.
1 The following key figures and explanations are based on OECD health data and corresponding OECD publications; the available data refer to the year 2022 or the latest available figures from the previous year.
Healthcare spending as % of GDP
Download(XLS, 35 KB)| in % | 2021 | 2010 | 2000 | 1990 | 1980 | 1970 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 16.6 | 16.3 | 12.5 | 11.2 | 8.2 | 6.2 |
| France | 12.1 | 11.2 | 9.6 | 8.0 | 6.8 | 5.2 |
| Germany | 12.7 | 11.1 | 9.9 | 8.0 | 8.1 | 5.7 |
| Switzerland | 11.3 | 9.9 | 9.1 | 7.6 | 6.4 | 4.8 |
| Spain | 10.4 | 9.1 | 6.8 | 6.1 | 5.0 | 3.1 |
| China | 5.7 | 4.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Source: OECD health data; the available data refers to the year 2022 or the most recent available values from the previous year. | ||||||
Our most important markets developed as follows:
The market for biopharmaceuticals, clinical nutrition, MedTech, generic IV drugs, and iV Fluids1
The market for biopharmaceuticals from the therapeutic areas of oncology and autoimmune diseases consisting of originator products and biosimilarsBiosimilarsA biosimilar is a drug that is “similar” to another biologic drug already approved. grew by approximately 6% to around €193 billion, of which Biosimilars market is €18 billion with a growth rate of 8% versus prior year. The acquisition of a majority stake in mAbxience significantly strengthens Fresenius Kabi in this growth market, in which the company participates through biosimilars and contract development and manufacturing of biopharmaceuticals. The market for biopharmaceuticals is a fast-growing and innovative segment, which will gain even more relevance for the care of patients going forward. Competitors in the biosimilars market for biopharmaceuticals include Sandoz, Biocon, Coherus, Alvotech, and Teva.
In 2023, the global clinical nutrition market reached a size of approximately €11 billion. Within Europe, the market experienced growth of around 4%, while emerging market regions exhibited even higher growth rates. Latin America2 saw a 14% increase in the clinical nutrition market, and Southeast Asia similarly demonstrated robust growth at approximately 10%. Despite these positive trends, there remains substantial additional global growth potential, as nutrition therapies are underutilized in patient care, despite established medical and economic benefits proven by studies. Clinical nutrition administration, particularly in cases of health- or age-related nutritional deficiencies, has the potential to reduce hospital costs through shorter stays. Fresenius Kabi, as a prominent player in enteral nutritionEnteral nutritionApplication of liquid nutrition as a tube or sip feed via the gastrointestinal tract. and the leading provider of parenteral nutritionParenteral nutritionApplication of nutrients directly into the bloodstream of the patient (intravenously). This is necessary if the condition of a patient does not allow them to absorb and metabolize essential nutrients orally or as sip and tube feed in a sufficient quantity., aims to capitalize on this growth potential. The company plans to introduce its clinical nutrition offerings in countries where it currently lacks a comprehensive range. By expanding its product portfolio and leveraging new distribution channels, Fresenius Kabi is poised to enhance its global presence.
Competitors in the global parenteral nutrition market include Baxter and B. Braun. In the enteral nutrition market, Fresenius Kabi competes with Abbott, Nestlé, and Danone, among others.
The MedTech Infusion and Nutrition Systems (INS) product portfolio of Fresenius Kabi is broad and composed of product groups such as infusion and nutrition pumps and their dedicated disposables, extended by IT-based solutions focusing on application safety, user workflows, increased therapy efficiency and interoperability with hospital systems, non-dedicated disposables, anesthesia monitoring devices, and dedicated sensors. The market for devices and related dedicated disposables is estimated to be around €5 billion with a growth rate of 4%. There is a significant further market for non-dedicated disposables. The MedTech INS product range will be developed regionally and thus be available in more countries, particularly in the United States with the acquisition of Ivenix. In the MedTech INS segment, Fresenius Kabi ranks among the leading suppliers worldwide. Competitors in the market for medical technology products include Baxter, B. Braun, Becton Dickinson, and ICU Medical.
The market for MedTech Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapies (TCT) grew by around 4% to about €4 billion. Fresenius Kabi is the leading company in the market for blood collections, which has recovered slightly compared to the previous year. Increased demand for plasma-derived therapies and autotransfusion treatments has resulted in attractive market growth; Fresenius Kabi holds top-three positions in both markets. Due to newly approved treatments, the cell and gene therapies segment is the fastest-growing market within TCT. With the continued success of LovoLOVOLOVO is a cell processing system to wash differentiated and undifferentiated white blood cells for laboratory and research use. It is designed to offer a simple, fast, and automated method to remove supernatant, add and reduce volume in a fully closed system., now used in two of the six FDA-approved CAR-T therapies and in one of all the remaining approved cell therapies (not specific to CAR-T) in the United States, our cell therapies business grew compared to the previous year. Competitors in the transfusion technology market include Terumo, Haemonetics, and Macopharma.
In 2023, the global market for generic IV drugs and IV fluids was around €50 billion3. With significant regional differences, the market generated low- to mid-single digit growth. Fresenius Kabi was able to enter additional segments of the global addressable market due to the expansion of our product portfolio in the areas of complex formulations, differentiated generics, and prefilled syringes, among others. Fresenius Kabi's competitors in the market for generic IV drugs include Pfizer, Sanofi, Sandoz, Viatris, and Hikma. Competitors in the market for infusion therapies include B. Braun and Baxter.
1 Market data is based on company research and refers to the markets relevant for Fresenius Kabi. This is subject to annual volatility due to currency fluctuations and patent expiries of original drugs in the IV drug market, among other things.
2 Due to hyperinflation in Argentina, market growth is presented excluding Argentina.
3 As in the previous year, the market definition also includes revenue of off-patent products.
The hospital market1
The market volume for acute hospitals in Germany in 2022, measured in terms of total gross costs, amounted to around €128 billion2. Of this, around 61% was attributable to personnel costs and 38% to material costs, which increased by around 6% and 4% respectively.
Based on the number of admissions, Helios Germany is the leading company in the German market for acute hospitals with a market share of around 6%3. The Helios clinics mainly compete with individual hospitals or local and regional clinic associations. Private competitors include Asklepios Kliniken, Sana Kliniken, and Rhön-Klinikum.
1 In each case, the most recent market data available refers to the year 2022 as no more recent data has been published: German Federal Statistical Office, 2022 data; German Hospital Institute (DKI) 2023, Krankenhaus Barometer 2023
2 The market is defined by total costs of the German acute care hospitals (gross), less academic research and teaching.
3 Measured by Helios Germanys’ number of acute care admissions in 2022 in relation to total admissions numbers in Germany in 2022 (German Federal Statistical Office, 2022 data)
The number of inpatient treatment cases in German hospitals rose again in 2022 for the first time since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. In total, 16.8 million cases were treated. Nevertheless, the figure was around 13% below the pre-pandemic year 2019.
The increase in the remuneration of hospital services in the German flat rate per case billing system (DRG system) is based on what is known as the change value (‘‘Veränderungswert’’). It is calculated on an annual basis. For 2023, the change value was 4.32% (2022: 2.32%).
The flat rates per case are used to determine the reimbursement of inpatients. The related nursing staff costs per case at the bedside have been carved out from the flat rates since 2020. The nursing staff costs are reimbursed in full based on the actual costs incurred by the care budget which is individually negotiated separately by the contractual partners as part of the overall budget negotiations.
Compared to the previous year, the economic situation of German hospitals has deteriorated. 54% of German hospitals posted losses in 2022 (2021: 43%). The proportion of hospitals with an annual surplus was only 35% (2021: 44%). The main reason for the deteriorating economic situation is the inflation-related general cost increases.
hospital beds by operator
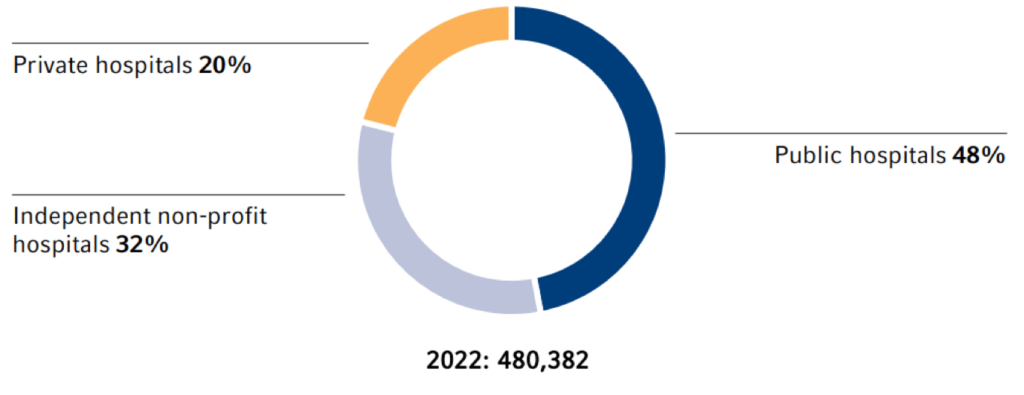
To provide financial support, hospitals in Germany were supplied with compensation and reimbursement amounts from the liquidity reserve of the healthcare fund for inflation-related additional costs in 2023. To determine the amount of the reimbursement, hospitals report the direct costs for the purchase of natural gas and electricity to the hospital planning authorities. For comparison, the energy discounts for the month of March 2022 are used. The financial support, which also extends to 2024, amounts to a total of €1.5 billion in hospital-specific reimbursement amounts and €4.5 billion in flat-rate compensation payments based on the number of beds (indirect costs).
Key figures for inpatient care in Germany
Download(XLS, 38 KB)| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2010 | 2000 | Change2022 / 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitals | 1,893 | 1,887 | 1,903 | 2,064 | 2,242 | 0% |
| Beds | 480,382 | 483,606 | 487,783 | 502,749 | 559,651 | -1% |
| Average length of stay (days) | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.9 | 9.7 | 0% |
| Number of admissions (millions) | 16.80 | 16.74 | 16.80 | 18.03 | 17.26 | 0% |
| Average costs per admission in €1 | 6,796 | 6,530 | 6,232 | 3,804 | - | 4% |
| 1 Values adjusted for miscoding in the equalization fund (Section 17a KHG) |
||||||
| Source: German Federal Statistical Office, 2022 data | ||||||
In addition to the often difficult economic and financial situation, there is an enormous need for investment. The German Hospital Institute (DKI) estimates that the annual investment requirements of German hospitals amount to about €7 billion.
The central topic in the German hospital sector in 2023 was the planned hospital structure reform. The aim of the reform is to fundamentally reshape the hospital landscape in Germany. The current system of purely volume-based remuneration via flat rates per case is to be changed. The plan is to limit remuneration based on flat rates per case to 40%. In future, an average of 60% of the remuneration is to be distributed independently of performance via what are known as maintenance flat rates (including the care budget).
The maintenance funding is to be linked to performance groups that are allocated to the individual hospitals by the federal states and which require compliance with defined criteria. Among other things, this is intended to ensure that complex treatments may only be carried out in hospitals that have the appropriate personnel and technical equipment. Depending on the performance group and with that, its relevance, hospitals will receive financial resources. The criteria for allocation have not yet been determined.
The changeover to the maintenance flat rates of 60% on average is expected to take place gradually over several years. The hospitals argue that the concept in its current form still only deals with operating costs, but not with the adequate financing of investment costs.
In July 2023, the federal and state governments agreed on a key points paper for the hospital reform. At the end of 2023, the Federal Ministry of Health presented a working draft for a law. The working draft is currently being examined by the participating federal states. The planned law is expected to come into force in the first quarter of 2024 at the earliest. Further information on the hospital structure reform can be found in the Outlook section. In 2023, the shortage of specialist staff and problems filling vacancies in the nursing care sector continued to pose a challenge for inpatient hospital care in Germany.
In 2023, the nursing staff minimum levels for nursing-sensitive wards were extended to include the areas of ear, nose, and throat medicine, urology, as well as rheumatology.
For the first time in 2023, day treatments without overnight stays in the hospital could be billed using flat rates per case. This is intended to reduce night shifts, particularly in nursing, in order to create additional capacity for nursing staff on the day shift.
In Spain, the private hospital market had a volume of around €20 billion in 20221.
With a sales share of around 12%, Helios Spain is the leading company in the private hospital market. Its competitors are a large number of privately run individual hospitals or smaller chains, including HM Hospitales, Hospiten, Vithas, Ribera Salud, Hospitales Sanitas, and HLA.
Of the approximately 800 hospitals in Spain, around two thirds of hospital beds are in public hospitals2. In an OECD comparison, Spain has around 3.0 beds per 1,000 inhabitants, which is well below the OECD average of 5.0 beds per 1,000 inhabitants.
Public healthcare facilities in Spain are largely tax-financed and are generally open to the population without further charges or co-payment obligations. In addition, the Spanish government promotes the private healthcare sector through tax reliefs for private health insurance purchased by employers, among other things.
After peaking in 2022, inflation in Spain decreased again in 2023. In particular, energy prices, which are also relevant for the hospital sector, stabilized at a significantly lower level in 2023.
A challenge in some regions of the country continued to be the shortage of skilled workers, particularly in the care sector, although the situation has improved significantly compared to during the waves of COVID-19. In addition, a certain shortage of doctors is emerging in some specialist areas due to the steadily increasing demand for healthcare services.
In addition to inflation-related cost increases, the shortage of specialists and changes in the regulatory environment, digitalization is another challenge for the hospital sector in Germany and Spain. At the same time, it offers enormous opportunities, for example by standardizing and automating processes to a greater extent. New technologies offer the possibility of tapping into efficiency potential while maintaining at least the same, and often even higher, quality and reducing costs. It is estimated that in Germany alone, around 12%3 of total expenditure on healthcare and patient care can be saved through digitalization.
The global market for fertility services was worth about €14.2 billion in 2022. The market is growing sustainably due to demographic and health trends as well as changing lifestyles. Significant scientific advances have led to higher success rates and lower burdens for patients. The global market for reproductive medicine is highly fragmented.
1 Market data based on company research and refers to the addressable market of Quirónsalud. Market definition includes both inpatient and outpatient healthcare services. It includes neither public-private partnership (PPP) nor occupational risk prevention centers (ORP). The market definition may differ from the definition in other contexts (e.g., regulatory definitions).
2 Healthcare in Spain (masainternational.de)
3 Digitalization in German hospitals McKinsey & Company, Healthcare September 2018
The market for projects and services for hospitals and other healthcare facilities
The general conditions for hospital planning and construction projects were again challenging in 2023 and continued to be characterized by supply bottlenecks, extraordinary cost increases, especially with regard to energy prices, and higher interest costs.
Fresenius Vamed meets these challenges through long-standing project partnerships, as well as its high level of expertise and experience in the fields of medical technology and operational and organizational planning. The service business also faced challenges in 2023 in terms of inflation-related cost increases and higher energy costs. Capacity restrictions, infection-related absences, and lower demand for rehabilitation services due to postponed elective surgeries played a slightly smaller role in 2023 than in the year before. Demand for reliable management of medical technology and high-end healthcare services remains robust.
The market for projects and services for hospitals and other healthcare facilities is very fragmented. Therefore, an overall market size cannot be determined. The markets are country-specific and depending, to a large extent, on factors such as public healthcare policies, government regulation, and levels of privatization, as well as demographics and economic and political conditions. In markets with established healthcare systems and mounting cost pressure, the challenge for healthcare facilities is to increase their efficiency. Here, demand is especially high for sustainable planning and energy-efficient construction, optimized hospital processes, and the outsourcing of medical-technical support services to external specialists. This enables hospitals to concentrate on their core competency − treating patients.
In addition to offering services for healthcare facilities worldwide, Fresenius Vamed itself is active as a leading post-acute care provider in Central Europe, especially in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and the Czech Republic. In emerging markets, the focus is on building and developing healthcare infrastructure and improving the level of healthcare.
Fresenius Vamed is a global company with no direct competitors covering a comparably comprehensive portfolio of projects, services, and total operational management over the entire life cycle of healthcare facilities. As a result, Fresenius Vamed has a unique selling proposition of its own. Depending on the business segment, the company competes with international companies and consortia, as well as with local providers.
Contact
Fresenius SE & Co. KGaA
Investor Relations
+49 (0) 6172 608-2485
ir-fre@fresenius.com

