The health care sector is one of the world’s largest industries and we are convinced that it shows excellent growth opportunities.
The main growth factors are:
- rising medical needs deriving from aging populations,
- the growing number of chronically ill and multimorbid patients,
- stronger demand for innovative products and therapies,
- advances in medical technology,
- the growing health consciousness, which increases the demand for health care services and facilities, and
- the increasing demand for digital health services for patients.
In the emerging countries, additional drivers are:
- expanding availability and correspondingly greater demand for basic health care, and
- increasing national incomes and hence higher spending on health care.
At the same time, the cost of health care is rising and claiming an ever-increasing share of national income. Health care spending averaged 9.7% of GDP in the OECD countries in 2020 (2019: 8.8%)1.
The United States had the highest per capita spending with US$10,9492 (2018: US$10,528). Germany ranked fourth among the OECD countries with US$6,5182 (2018: US$6,291). In Germany, 85% of health spending was funded by public sources in 2020, above the average of 76% in the OECD countries. Most of the OECD countries have enjoyed large gains in life expectancy over the past decades, thanks to improved living standards, public health interventions, and progress in medical care. In 2019, average life expectancy in the OECD countries was 81.0 years2 (2018: 80.7).
1 OECD Health Data
2 The latest available data from OECD Health Data refers to 2019, as no more recent data has been published.
Health care structures are being reviewed and cost-cutting potential identified in order to contain the steadily rising health care expenditures. However, such measures cannot compensate for the cost pressure. Market-based elements are increasingly being introduced into the health care system to create incentives for cost- and qualityconscious behavior. Overall treatment costs will be reduced through improved quality standards.
In addition, ever-greater importance is being placed on disease prevention and innovative reimbursement models linked to treatment quality standards.
Health care spending as % of GDP
Download(XLS, 35 KB)| in % | 2020 | 2010 | 2000 | 1990 | 1980 | 1970 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 16.8 | 16.3 | 12.5 | 11.2 | 8.2 | 6.2 |
| France | 12.4 | 11.2 | 9.6 | 8.0 | 6.8 | 5.2 |
| Germany | 12.5 | 11.1 | 9.9 | 8.0 | 8.1 | 5.7 |
| Switzerland | 11.3 | 9.9 | 9.1 | 7.6 | 6.4 | 4.8 |
| Spain | 9.0 | 9.1 | 6.8 | 6.1 | 5.0 | 3.1 |
| China | 5.1 | 4.4 | 4.5 | – | – | – |
| Source: The latest available data from OECD Health Data refers to 2020, as no more recent data has been published; database for USA, Switzerland, and Spain 2019 and China 2018. | ||||||
Our most important markets developed as follows:
The dialysisDialysisForm of renal replacement therapy where a semipermeable membrane – in peritoneal dialysis the peritoneum of the patient, in hemo dialysis the membrane of the dialyzer – is used to clean a patient’s blood. market
In 2021, the global dialysis market (products and services) was worth approximately €79 billion.
Worldwide, approximately 4.7 million patients with chronic renal failure were treated in 2021. Of these patients, around 3.8 million received dialysis treatments and about 890,000 were living with a transplanted kidney. About 89% were treated with hemodialysis, 11% with peritoneal dialysis.
The major growth driver is the growing number of patients suffering from diabetes and high blood pressure, two diseases that often precede the onset of chronic kidney failure. The number of dialysis patients worldwide increased by around 2% in 2021.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Fresenius Medical Care already reported increased mortality among patients in 2020. As a result of the global spread of the delta variant, COVID-19-related excess mortality increased again in the second half of 2021. This results in a total excess mortality of approximately 30,000 patients since the start of the pandemic.
The prevalence rate, which is the number of people with terminal kidney failure treated per million population, differs widely from region to region. The significant divergence in prevalence rates is due, on the one hand, to differences in age demographics, incidence of renal risk factors, genetic predisposition, and cultural habit, such as nutrition. On the other hand, access to dialysis treatment is still limited in many countries. A great many individuals with terminal kidney failure do not receive treatment and are therefore not included in the prevalencePrevalenceNumber of all patients who suffer from a specific disease within a defined period. The prevalence rate indicates the number of people with this specific disease (e.g., terminal kidney failure) treated per million population. statistics.
Market data on the dialysis market based on company's own surveys
Dialysis Services
In 2021, the global dialysis care market (including renal pharmaceuticals) was worth around €64 billion.
About 9% of worldwide dialysis patients were treated by Fresenius Medical Care. With 4,171 dialysis clinics and more than 345,000 dialysis patients in around 50 countries, Fresenius Medical Care operates by far the largest and most international network of clinics for the treatment of dialysis patients. In the United States, Fresenius Medical Care treated approximately 37% of dialysis patients in 2021. The market for dialysis care in the United States is already highly consolidated.
Outside the United States, the market for dialysis care is much more fragmented. Here, Fresenius Medical Care competes mainly with clinic chains, independent clinics, and with clinics that are affiliated with hospitals.
Dialysis reimbursement systems differ from country to country and often vary even within individual countries. The public health care programs, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), cover the medical services for the majority of all dialysis patients in the United States.
To be able to continue care for patients during the COVID-19 pandemic, Fresenius Medical Care implemented a number of measures, both operational and financial, to maintain an adequate workforce, protect patients and employees through expanded personal protective equipment protocols, and cover expenses related to surge capacity for dialysis patients suspected of having or confirmed to have COVID-19.
Dialysis products
In 2021, the global dialysis products market was worth around €15 billion.
Fresenius Medical Care is the leading provider of dialysis products in the world, with a market share of 36%.
Fresenius Medical Care is the leading supplier worldwide of hemodialysis products, with a market share of 42%, and has a market share of approximately 16% in the worldwide market of products for peritoneal dialysis.
Severe COVID-19 cases often cause acute kidney failure, which has significantly increased worldwide demand for dialysis solutions needed to conduct acute dialysis.
Renal care continuum, critical care solutions, and complementary assets
With our strategy 2025, we intend to achieve the next level and provide health care for chronically and critically ill patients across the entire renal care continuum. We aim to use our innovative, high-quality products and services to offer sustainable solutions at a reliable cost. To achieve this, we will concentrate on three key areas: the renal care continuum, critical care solutions, and complementary assets.
Fresenius Medical Care aims to implement new renal care models by applying state-of-the-art digital tools to give our business a major boost in terms of personalized dialysis and therapeutic innovations. Fresenius Medical Care also intends to treat more patients in their homes by offering holistic home care.
In addition, Fresenius Medical Care’s value-based care models create medical value while ensuring that care remains affordable and will incorporate kidney transplants in future. To achieve this, Fresenius Medical Care builds sustainable partnerships with payors worldwide to support the transition from a fee-for-service to a pay-for-performance system. In addition, Fresenius Medical Care Ventures GmbH therefore makes strategic investments in start-ups to gain access to new technologies in our core and complementary businesses, as well as new therapy approaches.
The number of patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy to treat acute renal failure is set to rise to more than 1.6 million p.a. by 2030. Over the next few years, we will leverage our competence in the business of critical care solutions to address a variety of health challenges. We can also use our expertise in the area of extracorporeal blood treatment for acute renal failure to treat acute heart and lung failure. We are also planning innovative solutions for multi-organ support to benefit from the growing critical care market.
Creating additional medical value while cutting costs requires complementary assets and solutions. We have reached some important milestones and gained many insights into how to coordinate patients more efficiently. We will continue to leverage our core competencies through partnerships, investments, and acquisitions.
A reasonable estimate of the market volume of the renal care continuum, critical care solutions, and complementary assets is not possible due to the large number of different services. The spectrum of our value-based care services may vary across countries and regions, depending on the particular reimbursement system or market specifics.
The market for generic IV drugs, biopharmaceuticals, clinical nutrition, infusion therapy, and medical devices / transfusion technology1
The global market for generic IV drugs, biopharmaceuticals, nutrition and infusion therapies, and medical devices/transfusion technology was worth about €114 billion in 2021.
Of this amount, around €42 billion2 was attributable to the global market for generic IV drugs. Fresenius Kabi was able to enter additional segments of the global addressable market due to targeted investments and the expansion of our product portfolio in the areas of complex formulations, liposomal solutions, and prefilled syringes, among others.
The global market for generic IV drugs generated low double-digit growth as it recovered from the 2020 market downturn as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak.
Competitors of Fresenius Kabi in the market for generic IV drugs include Pfizer, Sanofi, Sandoz, Viatris, and Hikma.
1 Market data is based on company research and refers to the markets relevant for Fresenius Kabi. This is subject to annual volatility due to currency fluctuations and patent expiries of original drugs in the IV drug market, among other things.
2 As in the previous year, the market definition also includes sales of off-patent products.
The market for biopharmaceuticals from the therapeutic areas of oncology and autoimmune diseases addressed by Fresenius Kabi grew by approximately 6% to around €51 billion in 2021. Today, more than one in three new drug approvals is a biopharmaceutical and significant growth of this global market, including biosimilars, is expected in the next few years and decades.
In 2021, the global market for clinical nutrition was worth about €10 billion. In Europe, this market grew by about 3%. Growth rates in emerging market regions were higher. In Latin America, the market for clinical nutrition grew by around 10%. Similarly strong growth of around 9% was realized in the Africa region. The market for clinical nutrition in Asia-Pacific increased by about 5%.
There is growth potential in clinical nutrition worldwide, because nutrition therapies are often not yet sufficiently used in patient care, although studies have proven their medical and economic benefits. In cases of health- or age-induced nutritional deficiencies, for example, the administration of clinical nutrition can reduce hospital costs through shorter stays.
In the market for clinical nutrition, Fresenius Kabi is one of the leading suppliers worldwide. Fresenius Kabi is the global market leader in the parenteral nutritionParenteral nutritionApplication of nutrients directly into the bloodstream of the patient (intravenously). This is necessary if the condition of a patient does not allow them to absorb and metabolize essential nutrients orally or as sip and tube feed in a sufficient quantity. product segment and intends to expand this position through products, offers, and services with high differentiation potential. In the enteral nutritionEnteral nutritionApplication of liquid nutrition as a tube or sip feed via the gastrointestinal tract. product segment, the company is a leader in Europe, Latin America, and China. The company intends to focus its enteral nutrition offerings more strongly than before on the regions where its product and service offerings have not yet or hardly been represented and launch them there. With the existing range and newly developed products as well as the entry into new distribution channels, Fresenius Kabi will serve the patient needs of the future.
In parenteral nutrition, competitors include Baxter, B. Braun, JW Pharma, and Kelun Pharmaceuticals. In the market for enteral nutrition, Fresenius Kabi competes with, among other companies, Abbott, Nestlé, and Danone.
The market for infusion therapies was worth about €5 billion in 2021, growing by 5%. In 2021, there was an increased demand for standard solutions in Asia-Pacific. In Europe, the infusion therapies market grew slightly, while business in the United States remained stable. Fresenius Kabi is the market leader in infusion therapies in Europe and Latin America.
Competitors in the market for infusion therapies include B. Braun and Baxter.
The market for medical devices in 2021 was slightly above the previous year’s level, at around €4 billion. In the medical devices market, the growth drivers are primarily IT-based solutions that focus on application safety and increased therapy efficiency. In the future, Fresenius Kabi will focus on the continuous further development of its product range and, in doing so, take into account the increasing proportion of software in the field of medical devices and its areas of application. In addition, the MedTech product range will be developed regionally and thus be available in more countries. In the medical devices segment, Fresenius Kabi ranks among the leading suppliers worldwide.
Competitors in the market for medical devices include Baxter, B. Braun, Becton Dickinson, and ICU Medical.
The market for transfusion technology grew by around 6% to 7% to around €3.5 billion compared with a weak previous year. Although blood and plasma donations recovered slightly compared to the previous year and demand for blood bags and plasma disposable products is on the rise again, they have not yet returned to the levels seen before the COVID-19 pandemic, even in 2021. The need for autotransfusion treatments has decreased further compared to the previous year due to operations still being postponed. The pandemic continued to have a slightly positive impact on the demand for convalescent plasma. A potential therapy option for some COVID-19 patients is based on the use of plasma (blood component) in patients who have recovered. This process is made possible by devices from our portfolio such as Alyx. In transfusion technology, Fresenius Kabi is one of the world’s leading companies.
Competitors in the market for transfusion technology include Terumo, Haemonetics, and Macopharma.
The hospital market1
The market volume for acute care hospitals in Germany in 2019 was around €111 billion2, as defined by total costs (gross). Personnel costs accounted for around 61% of this total and material costs for 37%, each of which increased by around 6%.
With a share of sales of around 6%3, Helios Germany is the leading company in the German market for acute care hospitals. The company’s hospitals compete primarily with individual hospitals or local and regional hospital associations. The main private competitors are Asklepios Kliniken, Sana Kliniken, and Rhön-Klinikum.
1 In each case, the most recent market data available refers to the year 2019 as no more recent data has been published: German Federal Statistical Office, 2019 data; German Hospital Institute (DKI), Krankenhaus Barometer 2021
2 The market is defined by total costs of the German acute care hospitals (gross), less academic research and teaching.
3 Measured by 2021 sales in relation to gross total costs of acute care hospitals minus scientific research and teaching in Germany (latest available data: Federal Statistical Office, 2019 data)
hospital beds by operator
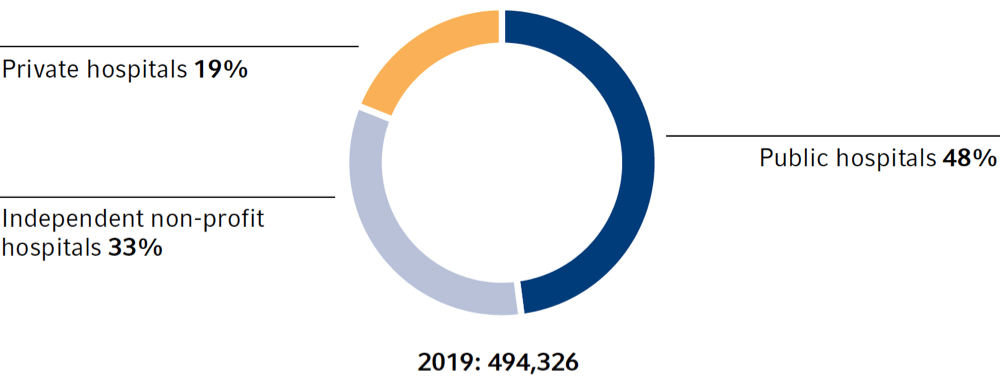
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the number of inpatient treatments in German hospitals in 2020. A total of 16.4 million admissions were treated, around 13% fewer patients than in the previous year.
The economic situation of German hospitals overall improved in 2020 compared with the previous year. While the pandemic led to significantly fewer admissions, the hospitals received some financial support to partially compensate for the negative effects of COVID-19. Expectations for 2021, however, are significantly more negative: around 60% of hospitals expect to record losses in 2021. 23% project to break even and just 17% expect to be able to generate a profit for the year. The main reason for the worsening economic situation is the COVID-19-related revenue loss among hospitals.
In addition to the often difficult economic and financial situation, there is an enormous need for capital expenditure due to medical and technological advances, higher quality requirements, and necessary building renovations, as well as investments in digitalization and increasing sustainability efforts1. Moreover, the federal states have in the past failed to meet their statutory obligation to provide sufficient financial resources. The German Hospital Institute (DKI) estimates that the annual investment requirement at German hospitals is over €6 billion. This is more than two times the investment funding currently being provided by the federal states.
1 Roland Berger, Krankenhausstudie 2021
What is known as the change in value figure is crucial for the increase in reimbursement for hospital treatments. It is used to compensate for rising costs in the hospital market, particularly with regard to personnel and material costs. The change in value figure is redetermined each year for the following year. For 2021, it was 2.53% (2020: 3.66%).
For the first phase of the COVID-19 pandemic until the end of September 2020, what was referred to as the German law to ease the financial burden on hospitals (“Krankenhaus Rettungsschirm“) was passed as an instrument of economic support for hospitals. Among other things, the law provided for a compensation lump sum for each bed kept free per day of occupancy. In various follow-up regulations, the conditions for the financial assistance were adjusted until they expired mid of June 2021. In addition, a full-year offset was implemented to compensate for COVID-19-related revenue shortfalls (Corona compensation). The reference figure is the hospital-specific revenue from 2019. Due to the sharp rise in COVID-19 infection levels and hospital admissions in the fall of 2021, those hospitals that kept beds free for the treatment of COVID-19 patients or that were heavily burdened due to the interregional transfers of ICU patients within what was referred to as the “Kleeblattsystem” again received compensation payments starting in November.
Key Figures for Inpatient care in Germany
Download(XLS, 36 KB)| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2010 | 2000 | Change 2019 / 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitals | 1,914 | 1,925 | 1,942 | 2,064 | 2,242 | 0% |
| Beds | 494,326 | 498,192 | 497,182 | 502,749 | 559,651 | -1% |
| Length of stay (days) | 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 9.7 | 0% |
| Number of admissions (millions) | 19.41 | 19.39 | 19.44 | 18.03 | 17.26 | 0% |
| Average costs per admission in €1 | 5,926 | 5,615 | 5,439 | 4,432 | 3,216 | 6% |
| 1 Total costs, gross | ||||||
| Source: German Federal Statistical Office, 2019 data | ||||||
Digitalization in hospitals in Germany is to be driven forward with the Hospital Future Act (“Krankenhauszukunftsgesetz”). For example, nationwide standards will be introduced to better interlink the health care system and to further improve patient care. Funding is being provided for investments in modern emergency room capacities and digital infrastructure, e.g., patient portals, electronic documentation of nursing and treatment services, digital medication management, IT security measures, and cross-sector telemedical network structures.
In 2021, the electronic patient file (ePA) was introduced on a mandatory basis. This also creates an obligation for hospitals to become connected to the telematics infrastructureTelematics infrastructureThe telematics infrastructure is intended to network all those involved in the German health care system and enable a secure exchange of information across sectors and systems. (TI), which is intended to standardize and simplify the exchange of data between players in the health care system. Hospitals must store patient-related data digitally or make it available via the ePA.
In 2021, the minimum level for nursing staff in the care-intensive units introduced in 2019 was expanded to include internal medicine, general surgery, pediatrics, and pediatric intensive care. Previously, the minimum level for nursing staff already applied in the areas of geriatrics, intensive care, cardiology, trauma surgery, cardiac surgery, neurology, early neurological rehabilitation, and neurology / stroke unit wards.
Due to the regulations of the Act to Strengthen Nursing Staff (“Pflegepersonalstärkungsgesetz”), since 2020, nursing costs have been deducted from the standardized base rates and the costs for direct nursing patient care are instead fully reimbursed by the health insurance companies via separate care budgets at costs. In December 2020, the German Hospital Federation (DKG) and the German Association of Statutory Health Insurance Funds (GKV-SV) concluded a new agreement on the separation of nursing staff costs for 2021 (“Pflegepersonalabgrenzungsvereinbarung”). Following various amendment agreements, a narrower definition (interpretation) of nursing staff costs went into effect for the full year 2021. In July 2021, the legislator created the foundation for nursing budgets for 2020 to also be negotiated according to the new regulations (“Gesundheitsversorgungsweiterentwicklungsgesetz – GVWG”). Only those hospitals that had concluded a written agreement on the care budget before the GVWG came into force are exempt from the new regulations.
The private hospital market in Spain had a volume of around €16 billion1 in 2020.
Helios Spain is the market leader with a market share of around 12% in the private hospital market in terms of sales. Helios Spain competes with a large number of stand alone private hospitals as well as with smaller hospital chains such as HM Hospitales, Hospiten, Vithas, Ribera Salud, Hospitales Sanitas, and HLA, among other chains.
After high infection rates and health care overload, especially in the first half of 2020, the epidemiological situation in Spain improved and almost approached pre-pandemic normality in 2021. In particular, high vaccination readiness and a well-organized vaccination structure with large vaccination centers allowed the country to achieve a vaccination rate close to 80%, one of the highest in Europe2. As a result, hospitals recorded significantly fewer severe COVID-19 cases and the number of COVID-19 intensive care patients decreased significantly. Hospital operations continued to return to normal with increased safety measures. Even the rising incidences at the end of the year did not lead to constraints in patient care, and very few elective treatments were canceled.
1 Market data based on company research and refers to the addressable market of Quirónsalud. Market definition includes both inpatient and outpatient health care services. It includes neither public-private partnership (PPPPPP (public-private partnership model)Public-private partnership describes a government service or private business venture that is funded and operated through a partnership of government and one or more private-sector companies. In most cases, PPP accompanies a part-privatization of governmental services.) nor occupational risk prevention centers (ORP). The market definition may differ from the definition in other contexts (e.g., regulatory definitions).
2 The Lancet, News, Volume 9, Issue 12, E120, December 2021
Reimbursement for COVID-19 patients in 2021 remained largely unchanged from 2020. The treatment is generally negotiated bilaterally according to existing contracts, tariffs, and regulations between the private hospital operators and the private health insurers or the relevant government authorities.
The COVID-19 crisis has also accelerated the use of telemedicine in Spain, leading to an increase in video consultations. This trend will continue as, among other things, medical care can be improved and greater efficiency created in the health care system in this way.
The global market for fertility services was worth about €9 billion in 2020. Market growth is driven by demographic and health trends as well as changing lifestyles. Notable scientific advances in this field have led to higher success rates and less strain for patients. The global market for fertility services is highly fragmented, representing an attractive opportunity for consolidation.
The market for projects and services for hospitals and other health care facilities
The global market for projects and services for hospitals and other health care facilities was heavily impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic throughout 2021.
The general conditions for hospital planning and construction projects were again challenging and characterized by supply bottlenecks, extraordinary cost increases, and travel and quarantine restrictions. Due to long-standing project partnerships and a high level of competence and experience, Fresenius Vamed was able to meet these challenges.
The service business also faces challenges regarding the safety of employees and patients in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Capacity restrictions and lower demand for rehabilitation services due to postponed elective surgeries played a smaller role in 2021 than last year. Demand for reliable management of medical technology and high-end health care services remains robust.
The market for projects and services for hospitals and other health care facilities is very fragmented. Therefore, an overall market size cannot be determined. The market is country-specific and depends, to a large extent, on factors such as public health care policies, government regulation, and levels of privatization, as well as demographics and economic and political conditions. In markets with established health care systems and mounting cost pressure, the challenge for health care facilities is to increase their efficiency. Here, demand is especially high for sustainable planning and energy-efficient construction, optimized hospital processes, and the outsourcing of medical-technical support services to external specialists. This enables hospitals to concentrate on their core competency − treating patients.
In addition to offering services for health care facilities worldwide, Fresenius Vamed itself is active as a leading post-acute care provider in Central Europe, especially in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and the Czech Republic. In emerging markets, the focus is on building and developing health care infrastructure and improving the level of health care.
Fresenius Vamed is a global company with no direct competitors covering a comparably comprehensive portfolio of projects, services, and total operational management over the entire life cycle of health care facilities. As a result, Fresenius Vamed has a unique selling proposition of its own. Depending on the business segment, the company competes with international companies and consortia, as well as with local providers.

